

The remaining 67% present in the intracellular fluid. The Science of Nutrition, 3e (Thompson) Chapter 9 Nutrients Involved in Fluid and Electrolyte Balance 1) Approximately what percentage of the body is composed of fluid A) 10 - 20 B) 30 - 45 C) 50 - 70 D) 60 - 80 Answer: C Page Ref: 348 Skill: Remembering Learning Obj.: 9. 33% of body fluid is made up of extracellular fluid, 25% of which is interstitial fluid and the other 8% is plasma. The amount of each type of body fluid varies. The composition of the blood and the interstitial fluid is also very similar. Body fluids can be discussed in terms of their specific fluid compartment, a location that is largely separate from another compartment by some form of a physical barrier.The intracellular fluid (ICF) compartment is the system that includes all fluid enclosed in cells by their plasma membranes.Extracellular fluid (ECF) surrounds all cells in the body. 3 ), and carbon dioxide (CO 2) in order to maintain pH in the blood and duodenum, among other tissues, to support proper. The bicarbonate buffer system is an acid-base homeostatic mechanism involving the balance of carbonic acid (H 2 CO 3 ), bicarbonate ion (HCO. The plasma of the body has the same composition as the blood, with the exception of erythrocytes. Most of the carbonic acid then dissociates to bicarbonate and hydrogen ions. The extracellular fluid is sub-divided into two: These conditions are regulated by the mechanism of homeostasis. The intracellular fluid (ICF) is the fluid within cells. Concentrations of intracellular and extracellular cations are as follows: Intracellular potassium concentration. Extracellular fluid includes both the fluid component of the blood (called plasma ) and the interstitial fluid (IF) that surrounds all cells not in the blood (Figure 8.6).
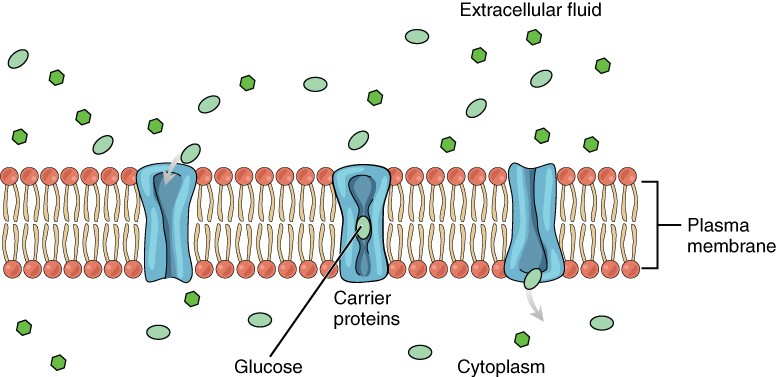
Because of this, the extracellular fluid must maintain relatively stable conditions, for example pH and concentrations of water, ions and glucose. The major extracellular cation is sodium. Extracellular fluid surrounds the cells and acts as a transition between an organism's external environment and the environment inside their cells, the intracellular fluid. The intracellular fluid consists mostly of water. The extracellular fluid is the watery internal environment of multicellular organisms. The extracellular fluid can be divided into two major sub compartments, interstitial fluid and blood plasma.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
